Educator Onboarding
LEO Art Challenge Workshop
ICE 2019: Satellite Tracking, Orbits, and Modeling
SEEC 2019: Satellite Tracking, Orbits, and Modeling
Workshop:ITEC Trek-a-Sat
Workshop: 2018-01-27 Yerkes
Workshop: 2017-10-28 Carthage-Yerkes Electrostatics in Space
Workshop: 2017-06-29-BTCI-Life in Space!
Workshop: 2017-03-11 Yerkes
Workshop: 2017-02-07 SEEC
Workshop: 2017-01-28 Yerkes
Tools You Might Use
Educational Learning
Standards
Documentation
Electrostatics in Space
Diagrama de temas
-
High energy charged particles can cause big troubles in space from space suits, to spacecraft electronics, to working in space. Activities in this course will include learning the origin, transfer, and measurement of electrostatic charges and its transportation within spacecraft materials.
-
Electrostatics in Space - What's the Concern?
Authors: Frances Dellutri, NSS Director of Education
Lynne Zielinski, NSS VP of Education
Summary: High energy charged particles can cause big troubles in space from space suits, to spacecraft electronics, to working in space. Activities in this course will include learning the origin, transfer, and measurement of electrostatic charges and its transportation within spacecraft materials.
Lesson Objectives: ( Middle School and High School)
1. Students will have a fundamental understanding of the origin importance of electrostatics and its presence, effects, and hazards in space.
2.They will also consider the technological advancements needed to use and occupy space to the fullest extent, by managing and mitigating electrostatics in space.
3.Students will add insight into the possibility of student careers that will address electrostatic challenges in material use in the exploration and use of space.
Students will be involved in the following activities:a. Determining the Average Velocity and Average Acceleration of a coronal mass ejecta carrying electrostatic charge.
b. Testing electrostatic induction and conduction with an electroscope
c. Experimenting with a material response to electrostatic charge with a portable Van de Graaff generator that levitates objects electrostatically.
Connections with Next Generation Science Standards and Common Core State Standards:
PS2-1
Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence of the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces on the motion of an object.
PS2-3
Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
Make observations and/or measurements of an object’s motion to provide evidence that a pattern can be used to predict future motion.
PS1-4
Structure and Properties of Matter
Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when temperature is removed.
PS2-3,5
Forces and Interactions
Ask questions about date to determine the factors that affect the strength of electric and magnetic forces.
PS-4
Waves and Electromagnetic Radiation
Develop and use a model to show that waves are reflected, transmitted, or absorbed through various materials
MS-ESS1-3
Space Systems
Analyze and interpret data to determine scale properties of objects in the solar system
PS3-1
Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
Apply scientific and engineering ideas to design, evaluate, and refine a device that minimizes the force on a macroscopic object during a collision.
Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions
Analyze data to support the claim that Newton’s second law of motion describes the mathematical relationship among the net force on a macroscopic object, its mass, and its acceleration.
CCSS
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
-
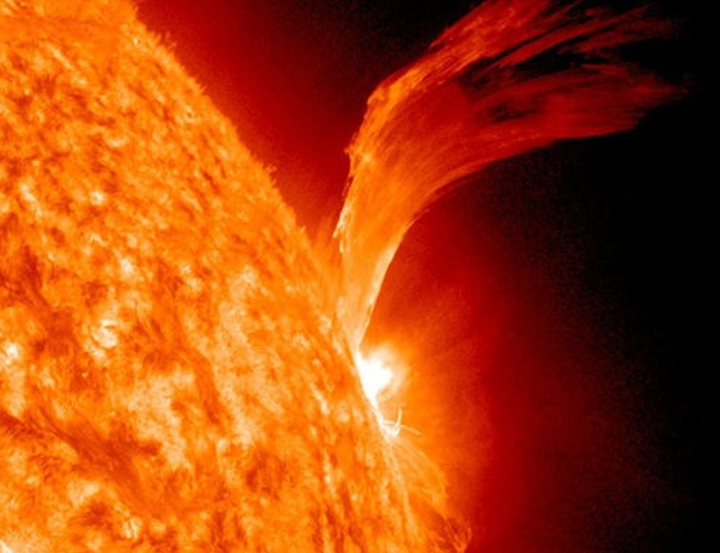 The sun has tremendous heat that is
pushing atoms together in a reaction called fusion. This is happening always. The sun is made up of plasma, superheated,
charged particles. The corona, the
outside of the sun sends enormous flares into the universe and that carries
plasma to us during a Coronal Mass Ejecta – a
CME. A solar proton event, or
"proton storm", occurs when particles emitted by the Sun become
accelerated either close to the Sun during a flare or in interplanetary space
by CME shocks. Lots of effects can be encountered in space and on Earth during a
SPE. Here's image from SOHO (NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory).
The sun has tremendous heat that is
pushing atoms together in a reaction called fusion. This is happening always. The sun is made up of plasma, superheated,
charged particles. The corona, the
outside of the sun sends enormous flares into the universe and that carries
plasma to us during a Coronal Mass Ejecta – a
CME. A solar proton event, or
"proton storm", occurs when particles emitted by the Sun become
accelerated either close to the Sun during a flare or in interplanetary space
by CME shocks. Lots of effects can be encountered in space and on Earth during a
SPE. Here's image from SOHO (NASA's Solar and Heliospheric Observatory).The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma consists of mostly electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. Embedded within the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field.
As the particles become superheated, the particles become charged and they have are elevated to a higher energy level. Atoms now carry an extra electron. But the charged condition is not stable and cannot be sustained in nature.
Two images shown below show the progression of a solar flare and wind:
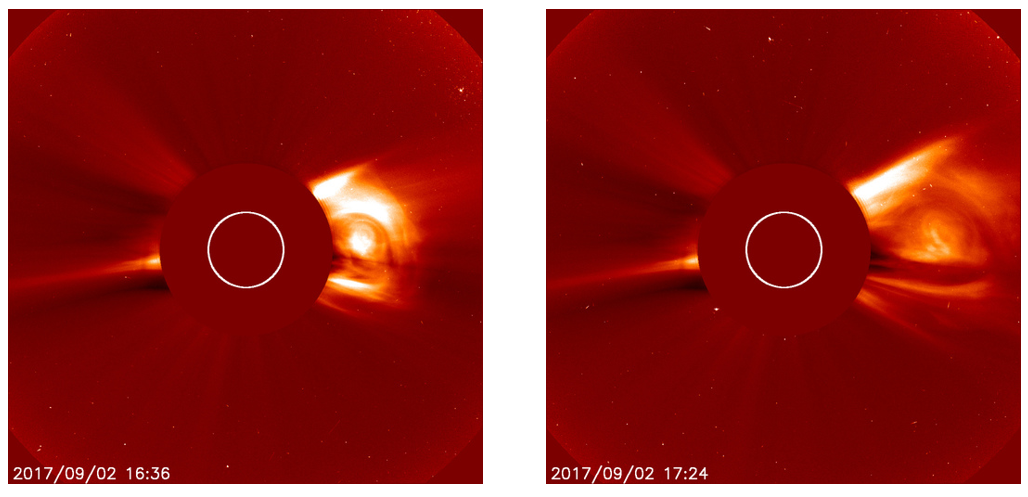

Students have the opportunity to determine the progression of the CME.
Attached are activities to determine the progression a feature within the solar plasma/wind for the Middle and High School Levels.
-
SPEs occur when charged particles in the Sun's atmosphere are accelerated to extremely high velocities. These charged
particles, referred to as solar energetic particles, can escape into interplanetary space where they follow the interplanetary magnetic field.
When solar energetic particles interact with the Earth's magnetosphere, they are guided by the Earth's magnetic field towards the north and south poles where they can penetrate into the upper atmosphere.
A Solar Energetic Particle Event is also known as a Solar Radiation Storm.
Magnetic Events move at a lower speed, than SPE and do not penetrate with to the degree as an SPE. Both are produced by the same phenomenon.
Space Station Astronaut Don Pettit noted the cause of the 'Astronaut Eye' (eye flashes) and its appearance.
“When a cosmic ray happens to pass through the retina it causes the rods and cones to fire, and you perceive a flash of light that
Further, Astronaut Pettit mentions what happens to the equipment INSIDE the spacecraft:is really not there. The triggered cells are localized around the spot where the cosmic ray passes, so the flash has some structure. A perpendicular ray appears as a fuzzy dot. A ray at an angle appears as a segmented line. Sometimes the tracks have side branches, giving the impression of an electric spark. The retina functions as a miniature Wilson cloud chamber where the recording of a cosmic ray is displayed by a trail left in its wake.”
"Free from the protection offered by the atmosphere, cosmic rays bombard us within Space Station, penetrating the hull almost as if it was not there. They zap everything inside, causing such mischief as locking up our laptop computers and knocking pixels out of whack in our cameras. The computers recover with a reboot; the cameras suffer permanent damage. After about a year, the images they produce look like they are covered with electronic snow. Cosmic rays contribute most of the radiation dose received by Space Station crews. We have defined lifetime limits, after which you fly a desk for the rest of your career. No one has reached that dose level yet.”
Quote from: Universe Today Magazine -
This is a great interactive opportunity to experience different types of electric discharge:
https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/balloons-and-static-electricity
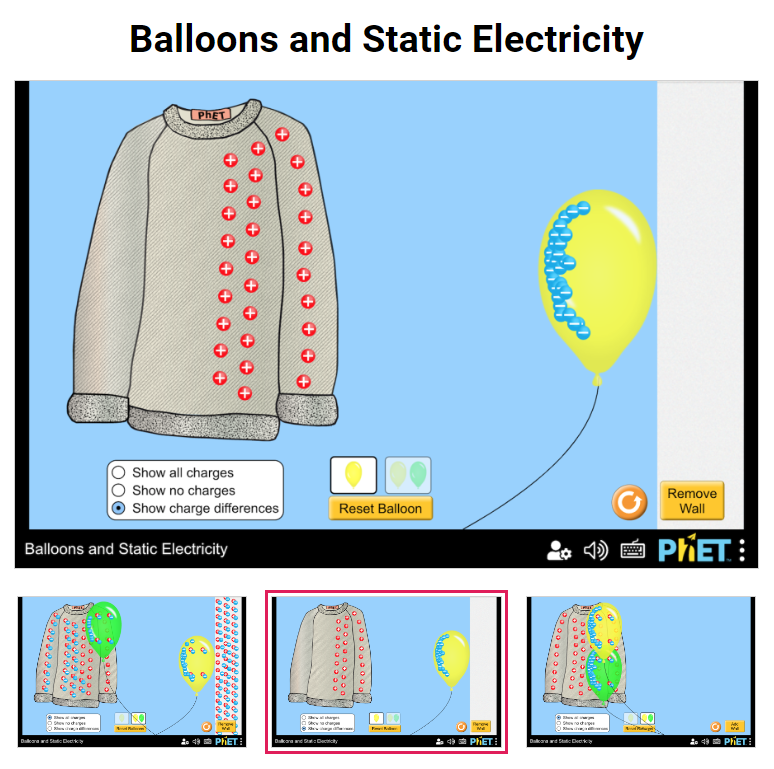
Ask students to explain what happens in the different representations, and with an additional ballooon.
-
This phet interactive on the location of electric charges and the fields that result is quite interesting.
https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/charges-and-fields
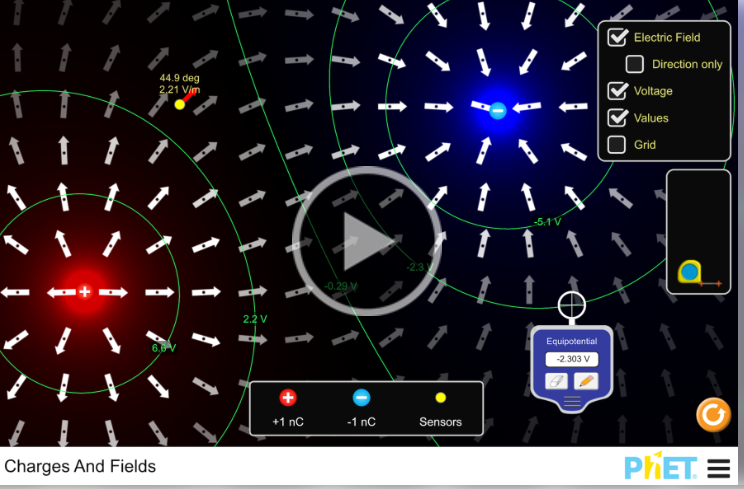
-
Imagine the different materials that could encounter electrostatics in space and their reaction to those forces.
How will it affect living and working in space?
-
Here's a great video explaining an electroscope and how it is affected by an electric charge.
Inductive and conductive (contacting) charges are discussed.
-
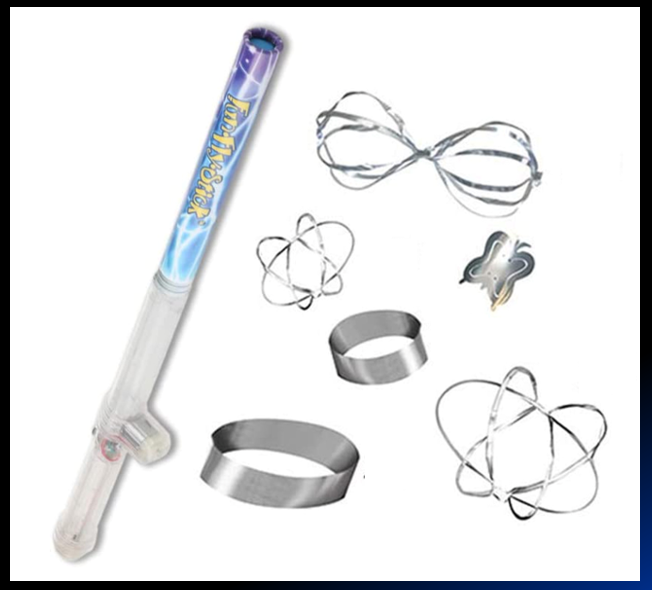
FunFlyer Sticks are a very fun way to experiment with electrostatic charge created from a portable Van der Graaf Generator!
These can be purchased: FunFlyer Sticks

-
Send a Postcard to Space through NSS Supported Blue Origin Club For The Future initiative!
Visit: SpacEdge Academy Postcards in Space Course

